Fatty liver: the earliest signs of cure and treatment
Fatty liver is an accumulation of excessive amounts in the liver, common in all ages. According to statistics, about 20-30% of the Vietnamese population has the fat test. If you do not time, can may be guide to many certificate variable to network features. Therefore, regular monitoring and monitoring of the liver enzymes is essential to keep the liver healthy.
9/8/2018 9:18:39 AM
1. Functions of the liver in the body
The liver is the second largest organ in the human body, behind the skin, located under the chest, and from the lungs by the diaphragm. Outside the liver structure there are many nerves but liver cells have no sensory nerves. Therefore, liver diseases usually do not have any certified properties, except in the case of loss of the liver, the external nerves are stretched, causing pain.
The liver has many functions for the body such as:
+ Metabolism: Glucid, Lipid, Protid.
+ Storage: blood, glucide, iron, vitamins A, D, B12.
+ Synthetic bile.
+ Purification and detoxification.
2. What is fatty liver?
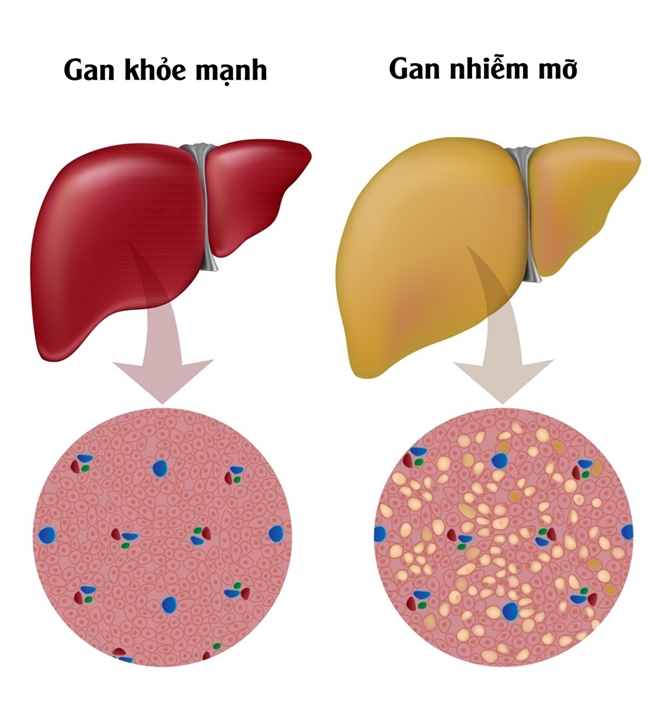
Fatty liver is a condition in which fat accumulates too much in the liver, 5% more than 2 - 4% as in the average person. The disease usually takes place silently so it is difficult to recognize, only detected during periodic health check, general ultrasound.
Healthy liver structure and fatty liver
The cause of fatty liver can be an unreasonable diet, stress, obesity or unscientific lifestyle. In the past, many people thought that fatty liver was harmless. However, this is a long-term, progressive medical condition, over 10 years and about 20% of cases turn into irreversible lesions such as cirrhosis, liver cancer.
Fatty liver has 4 levels:
Level 1:
The first stage of fatty liver, mild disease, and benign, does not affect much health. . The percentage of fat accounts for 5-10% of liver weight, non-inflammatory accumulation (normal AST, ALT).
Symptoms of the disease at this stage are not clear, mainly detected by examination. Therefore, the disease progresses silently, causing the amount of fat stored in the liver to accumulate more and more, causing many serious complications. However, if properly detected and treated, the liver can restore its function and be healthy again.
Level 2:
The percentage of fat accounts for over 10-25% of the liver weight, with inflammation (AST, ALT increases). The fat has spread to the liver tissues, the diaphragm, and reduces the margins of the veins in the liver. But this is still considered an early stage of the disease, is still not dangerous to the health but can quickly transition to level 3 if left untreated.
In stage 2, the patient also does not appear clinical signs of fatty liver that can only be detected by ultrasound or liver tomography.
Level 3
The percentage of fat accounts for over 25-30% of liver weight, with inflammation (AST, ALT increase). Fat tissue slows down the liver's detoxifying and metabolic functions, making it difficult to treat and recover.
Level 4:
As the last stage of the disease, fat accumulation is over 30% of the weight of the liver, damaged liver parenchyma, and irreversible fibrosis. These are the causes of cirrhosis and liver cancer.
Level 4 fatty liver is easier to detect because there are some clinical manifestations such as nausea, jaundice, indigestion, abdominal pain ... To restore damage to liver cells takes time. appropriate time and treatment.
Fatty liver is one of the causes of cirrhosis and liver cancer
3. Causes and risk factors for disease
The cause of the disease is not clear, but there are several groups of causes that lead to fatty liver such as:
-
Overweight.
-
Hypothyroidism.
-
Pituitary failure.
-
Diabetes.
-
Use of cancer drugs.
-
Gastric, intestinal surgery.
-
High cholesterol levels.
-
The amount of triglycerides in the blood is high.
-
Multi-function egg sad syndrome.
-
The lifestyle, the diet is not scientific.
-
Metabolic syndrome.
4. Symptoms of fatty liver
About 70% of fatty liver cases have no symptoms. If yes, it is usually atypical, specific to any one pathology, namely:
-
Anorexia.
-
Low-grade fever
-
Nausea.
-
Feeling full, full of stomach.
-
Tired of grease.
-
Heavily lower right flank.
The signs of fatty liver disease
5. Methods of diagnosis
- Image diagnosis (ultrasound, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging): Seeing images of fatty liver, but not fully assessing liver function and other damage to the liver.
- Blood tests: Evaluate the change of liver enzymes (elevated liver enzymes). Thanks to that, find out the causes of liver damage.
- Liver biopsy: During liver biopsy, the doctor performs anesthesia, using biopsy needles to remove a piece of liver organization to examine cytology. With this diagnostic method, your doctor can clearly identify the cause of fatty liver. But, because it is an invasive test, it is rarely used in clinical practice. Liver biopsy is only performed to diagnose fatty liver in cases where there are no symptoms but the patient has increased liver enzymes.
6. How to treat the disease effectively
Level 1 and 2 fatty liver can completely recover if the patient is screened early and treated properly. From stage 3 onwards, with intervention, the damage does not recover. Therefore, it is necessary to get treatment as soon as possible.
Fatty liver has no specific treatment, but it only treats the causes of the disease well. Specifically:
-
The obese and sedentary people need to actively lose weight, increase mobility, and adjust the diet.
-
Liver damage due to drug use, need to switch to using drugs with less damage to the liver.
-
Having endocrine diseases, needing complete treatment of endocrine diseases.
-
Fatty liver caused by post-surgery, malnutrition, should adjust the diet.
In addition, patients can also combine the use of antioxidant drugs in the liver, East-Y drugs. However, it is necessary to consult the treating doctor before use.
Note that treatment of fatty liver does not depend on blood lipids. Because, there are many cases of fatty liver but there is no disorder of lipid metabolism. The treatment of fatty liver is only combined with blood lipid lowering drugs when the lipid content in the blood increases. Therefore, use this drug only as directed by the Physician.
Periodic liver screening is essential for timely detection and treatment of potential risks of disease
7. Prevent fatty liver disease
To prevent fatty liver you should:
-
Enhance green vegetables: vegetables, greens, vegetables.
-
Spices: onion, garlic, green tea, artichoke.
-
Less sweet fruits: citrus fruits.
-
Use vegetable oil instead of animal fats such as soybean oil, sesame oil, bran oil, olive oil. Should eat directly, not cook.
-
Increase exercise 30 minutes / day: walking, swimming, badminton, cycling ...
-
Weight control.
-
Add fish to your diet.
-
Limit stress, overwork.
-
Build a reasonable living and resting regime.
-
Periodic health check, careful monitoring when having dyslipidemia.
In addition, should absolutely abstain from some foods and drinks such as:
-
Alcohol, beer, cigarettes.
-
Do not eat animal viscera, animal fat.
-
Red meats.
-
Foods high in starch.
-
Foods high in sugar like confectionery
Fatty liver is one of the dangerous liver diseases. Therefore, you should screen for liver disease periodically or as soon as the body shows abnormal signs to prevent serious development of the disease.
CarePlus International Clinic system is one of the many liver disease screening sites currently selected by many outstanding advantages such as:
-
Is a clinic system built on international standards from facilities, equipment to the team of doctors.
-
Offering a wide range of high quality outpatient services at affordable prices.
-
Doctor focuses on professional, clear advice.
-
Properly appoint medical interventions, explain thoroughly examination results, treatment procedures.
-
Give advice on living regimen, eating to help support treatment.
-
Close follow-up after examination.
Refer to CarePlus liver disease screening package: AT MEDICINE For more advice and appointment appointments, please visit website: https://careplusvn.com/en/ or contact Hotline 1800 6116 today now on!