PREVENTING LIVER CANCER STARTS WITH HEPATITIS B SCREENING
6/12/2025 9:01:14 AM
This article was medically reviewed by Dr. Đinh Thị Ngọc Minh – Hepatology & Gastroenterology Specialist | CarePlus International Clinic System.
📌 According to data from GLOBOCAN 2024, liver cancer is one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths in Vietnam, with over 26,000 deaths recorded annually. One of the primary causes of this disease is infection with the hepatitis B virus (HBV). Currently, an estimated 8.6 million Vietnamese people are living with chronic hepatitis B – equivalent to about 10% of the population – making Vietnam one of the countries with the highest HBV infection rates in the world.
1️⃣ Is hepatitis B a hereditary disease?
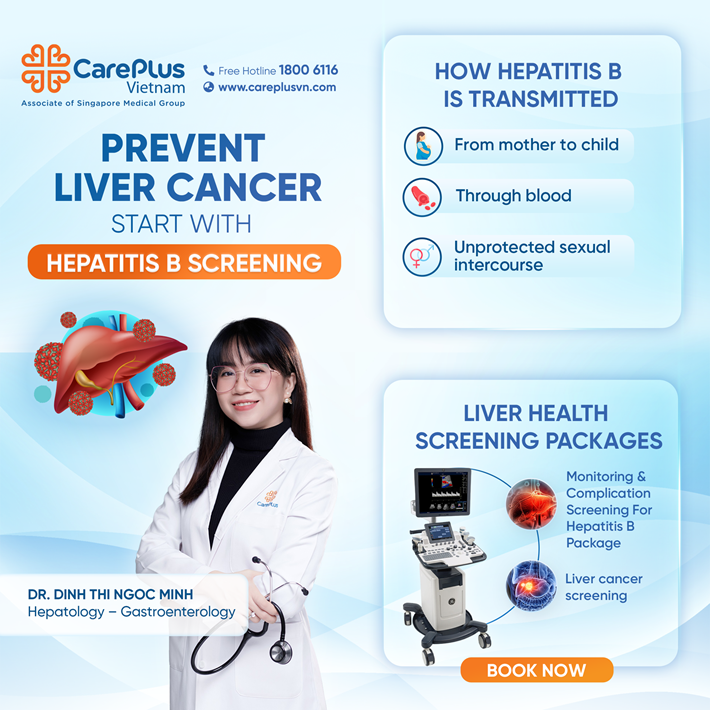
Many people mistakenly believe that hepatitis B is hereditary – meaning if the parents have it, the child will too. However, hepatitis B is actually a transmissible disease, not a genetic one. Transmission does not occur through eating, handshakes, or casual gestures like hugging or kissing, but only through the following three main routes:
🔹 Mother-to-child transmission: This occurs during childbirth when the baby is exposed to the mother's blood and secretions (the most common route in Vietnam), or more rarely during pregnancy if the mother has a very high viral load.
🔹 Blood transmission:Through sharing unsterilized needles, tattoo equipment, razors, ear-piercing tools, or manicure tools.
🔹 Unprotected sexual contact.
‼️ A major concern is that many people live with hepatitis B for years without showing any symptoms, thus unknowingly transmitting the virus to those around them.
2️⃣ The importance of hepatitis B screening in preventing liver cancer
🔸 Early detection: Regular screening helps detect the virus in its early stages, before it causes significant liver damage.
🔸 Risk assessment: Screening helps evaluate liver function through liver enzyme tests and imaging to detect early damage, allowing doctors to propose suitable treatment plans.
🔸 Preventing liver cancer in people diagnosed with hepatitis B:
• Not everyone requires treatment. Doctors will assess enzyme levels, viral load, liver fibrosis, and damage to determine the appropriate treatment plan.
• If medication is needed, modern antiviral drugs are effective, safe, affordable, and accessible.
• Regular monitoring is essential: Whether treated or not, patients must have check-ups and tests every 3–6 months as prescribed to prevent complications like cirrhosis or liver cancer.
🔸 For pregnant women:
• All pregnant women should be screened for hepatitis B during the first trimester. Early screening allows the mother and doctor to plan preventive measures to ensure the baby is born healthy and free from infection.
• If the mother is infected, she will receive preventive treatment starting at week 28 of pregnancy. The newborn will also be given vaccination and HBV immunoglobulin within the first 12 hours after birth to reduce transmission risk to nearly zero.
3️⃣ Effective prevention of hepatitis B through vaccination
Currently, vaccination against hepatitis B is considered the most effective prevention method. When administered following the doctor’s full vaccination schedule, the protection rate is up to 95%.
👉 Explore the full range of liver disease screening services at CarePlus here