Living with uterine fibroids
7/14/2021 4:31:34 PM
Uterine fibroids are fibroids that develop from the smooth and fibrous cells of the muscular layer of the uterus, and these tumours are not cancerous. Women can have one or more fibroids, and they can be the size of a pea or an egg and even have fibroids that grow the size of a melon.
Normally, when fibroids do not cause abnormal symptoms and repeat many times, they are not dangerous. However, due to the prevalence of fibroids, many women worry about complications from fibroids.
If you are having fibroids / uterine fibroids or suspect you have, please refer to the information below:
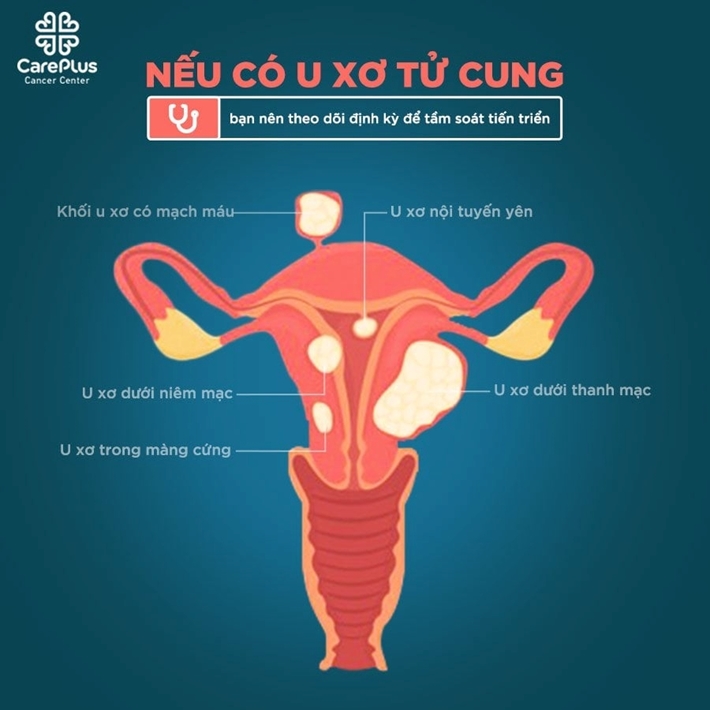
1️. Uterine fibroids and what causes uterine fibroids?
Uterine fibroids are a common gynaecological disease of all ages, especially women in the period of childbearing, pregnancy or menopause. Fibroids become more common in women between the ages of 40 and 50. After menopause, fibroids often shrink. No one knows what causes uterine fibroids. Research indicates that the hormones estrogen and progesterone control fibroids.
Factors that increase the risk of uterine fibroids include:
- Skin colour: All women are likely to get fibroids. However, black women have a higher risk of uterine fibroids, and fibroids are often larger, more numerous, and more variable.
- Genetics: If your mother or sister has fibroids, you are more likely to have them.
- Other factors: early menarche, vitamin D deficiency, a diet high in red meat and low in vegetables, fruits, dairy, and alcohol consumption appear to increase the risk of fibroids.
2. What are the symptoms of uterine fibroids?
Many women with fibroids/fibroids have no significant symptoms, but some have a lot of trouble. Common symptoms include:
- Pelvic pain and menstrual disorders such as hypermenorrhoea, heavy menstrual bleeding can lead to anaemia or the need for blood transfusion.
- Pressure on the bladder, causing frequent urination.
- Pressure on the rectum, causing constipation and back pain.
- Bloating, possibly due to a large fibroid pushing into the stomach area.
In addition to physical symptoms, women are also affected mentally when living with uterine fibroids. Many women suffer from depression, and anxiety reduces their quality of life.
3. Can uterine fibroids develop into cancer?
By definition, fibroids are not cancer. Fibroids do not seem to increase the risk of other uterine cancers, and fibroids often shrink after menopause. However, if you have fibroids/fibroids, you should have regular screening to monitor the progress of these tumours even though 99% of fibroids are benign.
4️. Do uterine fibroids affect fertility and pregnancy?
Most women with fibroids have normal pregnancies. If there are problems with pregnancy, they often arise due to the size and location of the fibroids, which can interfere with the embryo's implantation, making it difficult for you to get pregnant, miscarry or give birth prematurely. In some cases, the removal of a fibroid can help a woman get pregnant.
5️. Do uterine fibroids need treatment?
Because most women have no serious symptoms, most do not need treatment unless abnormal signs are repeated many times, affecting the quality of life. Unusual signs can be:
- Irregular vaginal bleeding
- Menstrual irregularity
- Vaginal discharge that has a bad smell changes color
- Pain, itching in the vagina
- Pelvic pain or difficulty urinating, frequent urination
There are 3 common treatment methods for fibroids/uterine fibroids:
🌿Treatment with natural methods helps reduce disease symptoms: For small fibroids, changing living habits, changing diet and exercising regularly also contribute positively to reducing the size. tumour. Some non-drug methods such as acupuncture, yoga, massage, herbal medicine, and hot compresses are also recommended for people with uterine fibroids. Eating healthy, reducing stress and losing weight (if obese) also have certain effects.
🌿 Drug treatment: Your doctor will prescribe medication to help regulate your hormone levels to reduce estrogen and progesterone. Some commonly used drugs such as birth control pills, hormonal drugs, GnRH antagonists, GnRH agonists,
🌿 SERMs.
Embolize the blood vessels feeding the fibroids with PVA, destroying the endometrium. A new method being applied is the destruction of fibroids by high-frequency ultrasound under the guidance of MRI.
Surgical treatment: Only applied when fibroids are too large and many other tumors are growing. At this point, the doctor will recommend surgery to remove the fibroids. If the fibroids continue to grow after surgery, they may need a hysterectomy to remove the fibroids again completely.
Register for Cancer Screening Package HERE