When should you consider getting tested for sexually transmitted diseases (STDs)?
STDs often have an incubation period before exhibiting external symptoms. You may unknowingly carry the infection without any awareness. Therefore, diagnostic testing for STDs is crucial for early detection and timely treatment.

6/20/2023 8:38:06 AM
When should you get tested for STDs?
If you have engaged in sexual contact with someone and notice any signs of an STD, it is important to visit a healthcare facility and consult with a doctor. STD symptoms may appear and disappear over time, but that does not mean the STD has gone away. Often, STD symptoms can be very mild and not bothersome, but it is still important to see a doctor if you notice anything unusual.
Different STDs have different symptoms. Signs of an STD may include:
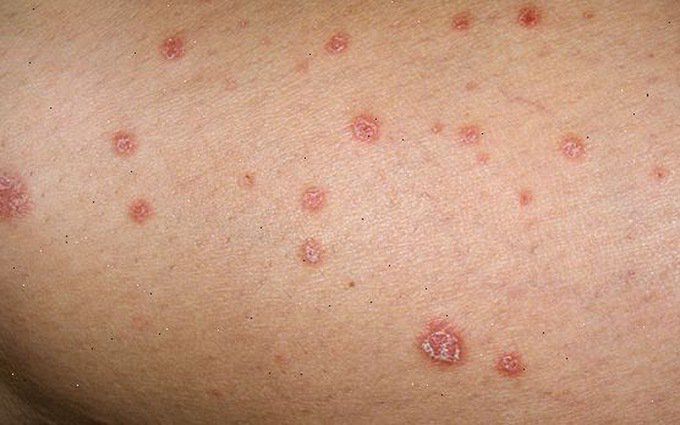
- Sores or bumps on the genital area, thighs, or buttocks
- Abnormal discharge from the vagina or penis
- Painful or frequent urination
- Itching, pain, irritation, and/or swelling in the penis, vagina, vulva, or anus
- Flu-like symptoms such as fever, body aches, swollen lymph nodes, and fatigue
All of these symptoms can also be caused by other non-STD-related conditions (such as pimples, urinary tract infections, or yeast infections). Therefore, testing is the only way to be sure of what is happening. Your doctor will help determine the specific tests you may need. Provide honest information to your doctor about:
Current symptoms
- Types of sexual contact you have engaged in (such as vaginal, anal, or oral sex, or any direct contact with the genital area)
- Use of condoms and/or dental dams
- If you suspect you have an STD, testing is crucial because some STDs can lead to serious health issues if left untreated. Additionally, having one STD increases the risk of acquiring other STDs, such as HIV. It is best to get tested immediately if you have an STD to prevent transmission to others.
Signs that indicate you should consider testing for STDs:
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) in the United States, you should consider testing for sexually transmitted diseases if you have had unsafe sexual intercourse with a partner who is not your spouse or a partner with an unknown sexual history.
You should get tested for STDs if you belong to any of the following groups:
You have had unsafe sexual intercourse with a partner who is not your spouse or a partner with an unknown sexual history.
Engage in high-risk sexual activities: Having multiple sexual partners or frequently changing partners, engaging in sex with other men if you are a man who has sex with men (MSM).
- You are pregnant or planning to become pregnant.
- Your body exhibits the following symptoms:
- Sharing needles, syringes, or blood transfusion with others.
- Unusual symptoms in the genital area such as sores, blisters, itching, irritation, redness, bleeding, or abnormal discharge.
- Other symptoms like fever, chills, swollen lymph nodes in the groin, joint pain, or rash.
- Abnormal vaginal or penile discharge.
- Itching, pain, redness, irritation, or the presence of abnormal sores in the anus or genital organs. These injuries may or may not be painful.
- Painful, burning, or frequent urination, or urinating more than usual.
- Unexplained lower abdominal pain unrelated to the menstrual cycle.
- Pain during intercourse or bleeding after sexual intercourse, etc.
Which STD tests should be performed?
Here is a brief summary of the recommendations for STD testing:
- All adults and adolescents aged 13 to 64 should be tested for HIV at least once.
- All sexually active women under 25 should be tested for gonorrhea and chlamydia annually. Women aged 25 and older with risk factors such as new sexual partners, multiple sexual partners, or a partner with an STD should also be tested for gonorrhea and chlamydia annually.
- All pregnant women should be tested early in pregnancy for gonorrhea, HIV, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C. Those at risk should also be tested for gonorrhea and chlamydia early in pregnancy. In some cases, retesting may be necessary.
- All men who have sex with men (MSM) and other individuals engaging in sexual activities with men should be tested:
- At least once a year for gonorrhea, chlamydia, and syphilis. Those with multiple or anonymous partners should be tested more frequently (e.g., every 3 to 6 months).
- At least once a year for HIV, and more frequent HIV testing is recommended if possible (e.g., every 3 to 6 months).
- At least once a year for hepatitis C if you are HIV-positive.
- Anyone engaging in sexual behaviors that put them at risk for infection or sharing needle injection for drug use should be tested for HIV at least once a year.
- Individuals engaging in oral or anal sex should discuss throat and rectal testing options with their healthcare provider.
The idea of testing may make you anxious, but try to think positively. Most common STDs can be easily cured with medication. While some STDs cannot be completely cured, they can be treated to reduce symptoms and the risk of transmission to others. So the sooner you know if you have an STD, the quicker you can start taking care of your own health and that of your partner.
If you have any of the symptoms mentioned above, you should get tested for STDs immediately. You should also get regular testing at least once a year to monitor your health status. Testing for STDs not only helps protect yourself but also protects your partners and loved ones. Remember: Prevention is better than cure!