What Are the Signs of Cervical Ectropion and When Should It Be Treated?
Cervical ectropion is a common physiological condition. It occurs when columnar epithelial cells (glandular cells) from inside the cervical canal are present on the outer surface of the cervix. This can lead to an increase in vaginal discharge and is typically detected during routine gynecological exams. Increased discharge combined with other risk factors can lead to cervicitis (inflammation of the cervix).
8/27/2024 9:01:04 AM
Recognizing the Signs of Cervicitis
Most women with cervical ectropion do not experience any distinct symptoms. However, some may notice increased vaginal discharge, itching, and abnormal-smelling or colored discharge, indicating infection that requires treatment.
Another sign is vaginal bleeding after intercourse, which can also be caused by other conditions like cervical polyps, vaginitis, cervicitis, or even cervical cancer. Thus, any unusual vaginal discharge should prompt a gynecological check-up to rule out other causes.
Causes of Cervicitis
Cervicitis often occurs in women who are sexually active, of childbearing age, or have recently given birth. In some cases, it may be congenital.
There are several causes of cervicitis:
- Gynecological infections: Conditions like gonorrhea, syphilis, genital warts, vaginitis, and cervicitis can lead to inflammation.
- Improper hygiene: Incorrect douching, using contaminated water, and poor hygiene during menstruation or after sexual intercourse can contribute.
- Lack of regular gynecological exams: Many women neglect routine check-ups. Mild conditions may go unnoticed and progress to more severe stages. Experts recommend a gynecological exam every six months to monitor reproductive health.
- Unhealthy sexual practices: Not using protection and having multiple sexual partners can cause injuries that may lead to infections if not promptly treated.
When Should Cervicitis Be Treated?
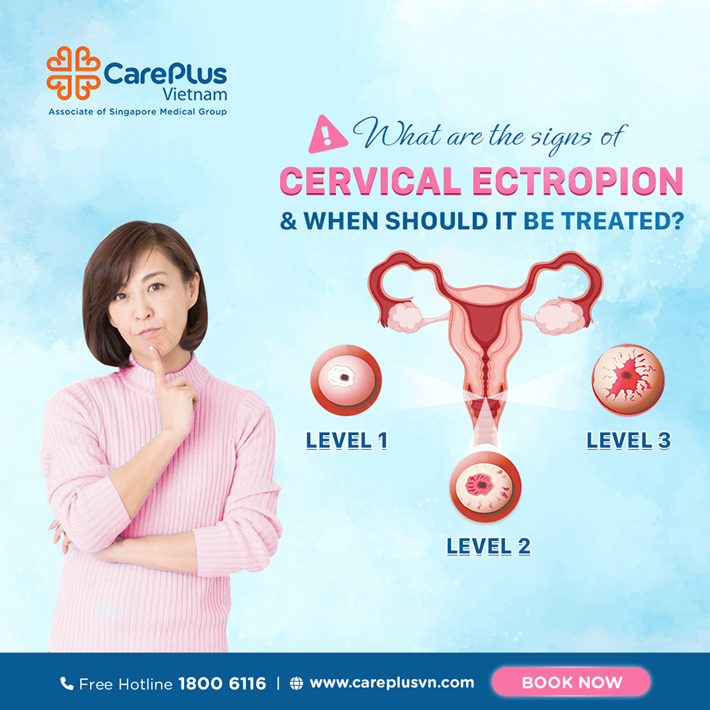
Cervicitis is classified into three levels, from mild to severe. Regular gynecological exams help doctors determine if treatment is necessary.
Level 1: Early-stage cervicitis involves the spread of glandular cells outside the cervical canal, encouraging bacterial growth. Symptoms include abnormal discharge (green, yellow, or milky white), sometimes with bubbles and a foul odor, and itching.
Level 2: Inflammation covers 50-70% of the cervix. Symptoms include vulvar pain, bleeding during intercourse, and potential complications like blocked fallopian tubes or cervicitis if untreated.
Level 3: Inflammation covers over 70% of the cervix, with more severe symptoms. Intercourse may cause pain and bleeding due to external glandular cells causing abrasions. Symptoms include:
- Increased, foul-smelling discharge with unusual color
- Non-menstrual vaginal bleeding
- Fatigue, irregular menstrual cycles, and abdominal pain like menstrual cramps
- Reduced sexual desire
Treatment depends on the individual’s response to the prescribed regimen. Options include medication or cauterization. Cauterization is only done after the infection is treated, but it can cause complications like scarring, narrowing of the cervical canal, and issues with menstruation, conception, and childbirth. Treatment methods are selected based on each specific case.
Cervicitis is a common condition among women. It’s important to pay attention to bodily changes and seek medical advice if you notice any unusual symptoms. Maintain good reproductive health by having regular gynecological exams, practicing proper hygiene, and leading a healthy sexual lifestyle.