What Are Lipids? The Dangers of Blood Lipid Disorders in the Body
8/27/2024 10:03:53 AM
1. What Are Lipids?
👉 Lipids, commonly known as fats, are esters formed between fatty acids and alcohols, essential components for human development. Lipids in food can be derived from both animal and plant sources. Plant-based lipids include margarine, refined oils, shortening, soybeans, peanuts, sesame seeds, etc. Animal-based lipids include eggs, meat, fish, and seafood. Generally, animal-based lipids are often referred to as fats, while plant-based lipids are usually called oils.
2. What Are Blood Lipid Disorders?
✅ Blood lipid disorders (also known as dyslipidemia, blood fat disorders, or lipid metabolism disorders) refer to an imbalance in one or more lipid parameters, commonly characterized by: ▪ High cholesterol ▪ High triglycerides ▪ High LDL-C ▪ Low HDL-C
✅ Blood lipid disorders often occur alongside and also serve as a risk factor for several cardiovascular, endocrine, or metabolic diseases. In many cases, individuals may experience a combination of various forms of these disorders.
3. What Causes Blood Lipid Disorders?
The causes of blood lipid disorders can be either primary or secondary.
Primary blood lipid disorders can occur at any age and include primary hypertriglyceridemia and mixed hyperlipidemia. Causes include:
🔸Gene mutations leading to excessive synthesis of cholesterol, triglycerides, or LDL-C, or reduced clearance of cholesterol, triglycerides, or LDL-C
🔸Gene mutations leading to reduced synthesis of HDL-C or increased clearance of HDL-C
Secondary blood lipid disorders are caused by lifestyle factors and metabolic, endocrine, liver diseases, or certain medications, such as:
🔸Lifestyle factors: Sedentary lifestyle, excessive alcohol consumption, high intake of foods rich in saturated fats, low fiber intake 🔸Diseases: Diabetes, Cushing's syndrome, hypothyroidism, chronic kidney disease, cirrhosis
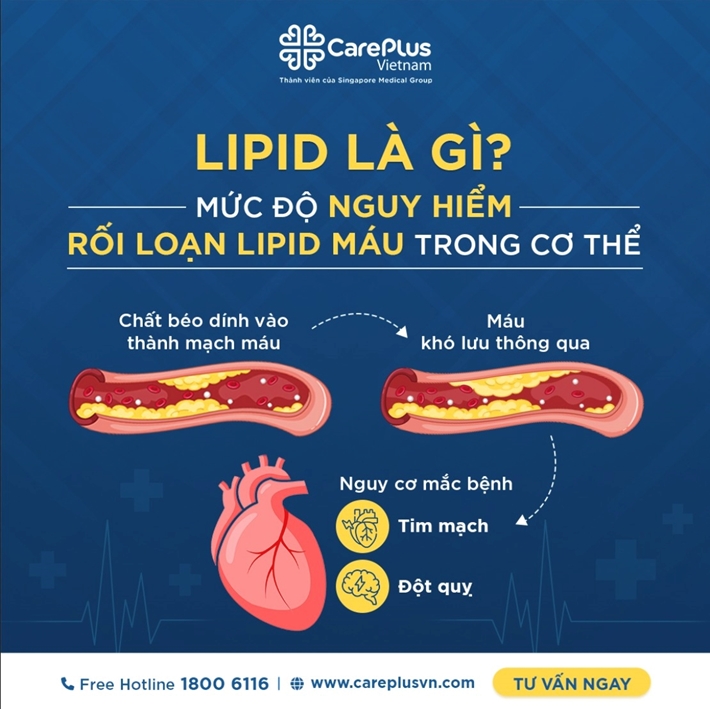
4. The Relationship Between Blood Lipid Disorders and Cardiovascular Diseases
✅ Atherosclerosis is the most significant complication of blood lipid disorders. It occurs due to the deposition of LDL cholesterol in the arterial walls, leading to thickening and hardening of the arteries, creating conditions for platelet adhesion, initiating blood clot formation, and arterial blockage. The consequences of coronary atherosclerosis include myocardial infarction, carotid atherosclerosis leading to stroke, and lower limb atherosclerosis causing inflammation, blockage, and foot tissue necrosis due to lack of blood flow.
✅ Blood lipid disorders increase the risk of overweight and obesity, hypertension, and diabetes—all of which are also risk factors for cardiovascular diseases. Therefore, a person diagnosed with a blood lipid disorder needs to be evaluated for other cardiovascular risks to implement effective treatment methods and prevent health complications.
Additionally, blood lipid disorders can lead to complications such as:
🔹Corneal arcus
🔹Xanthelasma
🔹Xanthomas under the skin: elbows, knees, hands, heels, bone membranes
🔹Retinal lipid deposits
🔹Fatty liver
🔹Acute pancreatitis (often due to elevated triglycerides)
5. Who Is at Risk for Blood Lipid Disorders?
The following groups are at risk for blood lipid disorders:
🔸Older adults
🔸Postmenopausal women
🔸Overweight or obese individuals
🔸Type 2 diabetics
🔸People with hypothyroidism
🔸Individuals with chronic kidney or liver disease
🔸Those with metabolic syndrome
🔸Individuals with Cushing's syndrome
🔸People with inflammatory bowel disease
🔸Smokers
🔸Those with a sedentary lifestyle
🔸People who consume a diet high in saturated and trans fats
🔸Alcoholics
🔸Individuals with parents who have blood lipid disorders
✨ In many cases, high blood lipid levels are only discovered after a stroke or other vascular event. Therefore, it is essential to have regular health check-ups, where doctors can assess cardiovascular risk, screen for blood lipid levels, and measure Lp(a) levels if you have the aforementioned risk factors.
💟 If treatment is indicated, it is important to follow the cardiologist's instructions, regularly monitor your condition, and undergo blood lipid and Lp(a) tests at CarePlus Clinics if you have risk factors. A team of specialized cardiologists will provide thorough examinations, necessary tests, and interventions, and manage other cardiovascular risk factors closely, with consultations and follow-up by a doctor: 🔸 Adopting a healthy diet to enhance cardiovascular health
🔸 Controlling body weight
🔸 Improving sleep quality
🔸 Limiting alcohol consumption
🔸 Quitting smoking
🔸 Exercising regularly
🔸 Reducing stress