How to care for a child with pneumonia at home
Whenever parents suspect their child's pneumonia symptoms listed below, take the child to see a doctor. Usually, pneumonia will be diagnosed through a clinical examination and lung auscultation. In unclear cases, blood tests and chest X-rays may be needed to make the diagnosis.

11/6/2023 1:28:21 PM
What is pneumonia?
Pneumonia is an inflammation of one or both lungs caused by a virus or bacteria.
When inflammation occurs, it will destroy the respiratory mucosa, increase mucus secretion, and swell small air ducts and alveoli in the lungs, causing congestion and reduced ventilation, leading to decreased blood oxygen. severe case
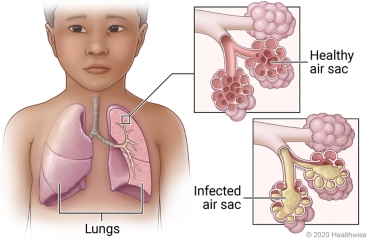
Signs of pneumonia
Depending on age and the cause of pneumonia, however, children will often have one of the following signs:
-
High fever
-
Cough a lot
-
Rapid breathing, difficulty breathing, convulsive breathing, or chest indentation: common in young children
-
Older children: fast breathing chest pain may occur when coughing
-
Non-respiratory symptoms: fatigue, abdominal pain, diarrhea, irritability, fussiness, loss of feeding...
When your child has the above signs, you need to take your child to the doctor immediately. Usually, pneumonia will be diagnosed through a clinical examination and lung auscultation. In unclear cases, blood tests and chest X-rays may be needed to make the diagnosis.
Caring for children with pneumonia at home
- Let the child rest
- Provide enough fluids (water, milk, juice, soup...)
- Compliance with antibiotic treatment: Enough days to completely treat the disease and reduce the risk of antibiotic-resistant bacteria
- Fever reduction: According to the doctor's instructions, do not use ibuprofen for children under three months old or dehydrated children.
- Limit cough medicine - even herbal medicine because it is ineffective. Many parents ask that cough suppressant medicine is not recommended because it will cause accumulation of mucus, leading to prolonged recovery.
- Avoid dusty environments and cigarette smoke
How to treat pneumonia?
Bacterial pneumonia: requires antibiotic treatment, average treatment time is 7-10 days, pneumonia symptoms usually improve after 48 hours of taking medication. Severe cases or poor response to oral antibiotics require hospitalization for injectable antibiotics or oxygen support.
After a full day of antibiotic treatment and the infection is gone, many children will still have a slight cough, gradually decreasing 2 to 3 weeks later. So parents should not worry if their child still coughs a few weeks after pneumonia.
Pneumonia caused by viruses: usually milder than bacteria, however, clinically it is difficult to clearly distinguish between viruses and bacteria, especially in cases of accompanying bacterial infection. Recovery from viral pneumonia is often slower and in many cases symptoms last up to 4 weeks to improve
How do we prevent pneumonia?
- Wash your hands with an antiseptic solution, and avoid touching your eyes, nose, and mouth
- Fully vaccinated: flu vaccine, pneumococcal vaccine...
- Limit contact with sources of infection in children with reduced resistance: malnourished children, children with underlying diseases
- Appropriate nutrition and physical exercise will be the best way to increase children's resistance.